Cancer treatments boosted by immune cell hacking
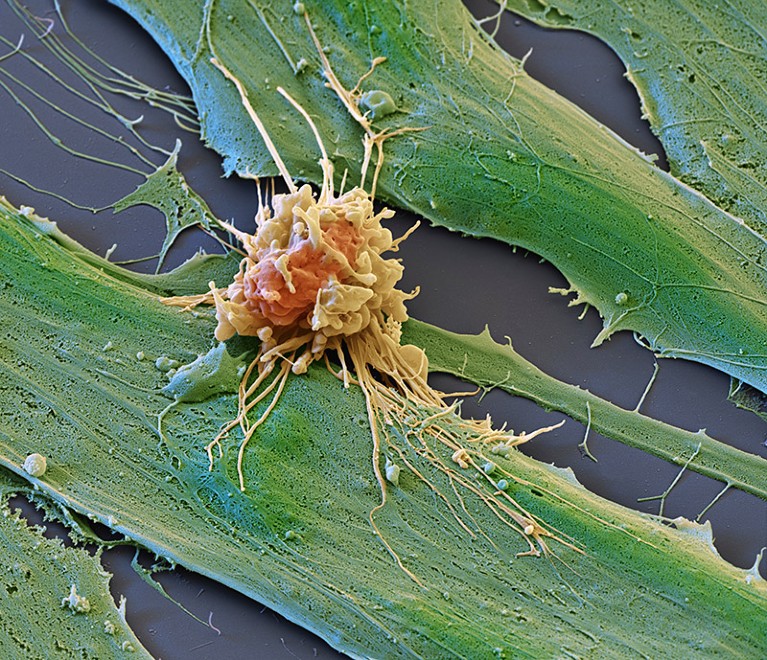
A Car T cell (orange) assaults a most cancers mobile (green).Credit score: Eye of Science/Science Photo Library
Elaborately engineered immune cells can not only recognize most cancers cells, but also evade defences that tumours use to fend off attacks, scientists have located.
Two reports revealed currently in Science1,2 create on the accomplishment of chimeric antigen receptor (Vehicle)-T cancer therapies, which use genetically altered T cells to search for out tumours and mark them for destruction. These solutions have the probable to guide to long-lasting remission, but are not productive for absolutely everyone, and have so significantly been successful versus only a tiny selection of cancers.
Past-vacation resort cancer treatment retains back again sickness for additional than a 10 years
To bolster the electricity of Vehicle-T therapies, scientists have even further engineered the cells to comprise switches that make it possible for command over when and exactly where the cells are lively. The hacked cells produce a protein that stimulates T cells, to counteract immunosuppressive alerts that are normally launched by tumours.
Both research are a tour de drive in T-cell engineering and spotlight the path that scientists want to force Automobile-T-cell therapy, suggests units immunologist Grégoire Altan-Bonnet at the US National Cancer Institute. “We know a great deal of the elements, now it’s staying able to put them collectively and check out,” he claims. “If we engineer the system effectively, we can genuinely place the tumours into checkmate.”
Engineered immune cells
T cells normally patrol the human body, hunting for overseas proteins exhibited on the area of cells. These cells could be contaminated with a virus, for instance, or they could be tumour cells that are manufacturing irregular, most cancers-connected proteins. A course of T cells known as killer T cells can then demolish the irregular cells.
Motor vehicle-T therapies entail genetically engineering T cells from a human being with most cancers to produce Cars, which are proteins that realize the proteins exhibited by tumour cells.
The tactic has been accredited to treat some leukaemias, lymphomas and myelomas. But researchers have been pursuing ways to make the remedies safer and a lot more efficient, and to extend their use to other ailments.
Remarkably mutated cancers reply better to immune therapy
In just one of the new scientific studies, Ahmad Khalil, a artificial biologist at Boston University in Massachusetts, and his colleagues wired a sophisticated procedure of 11 DNA sequences into Vehicle T cells. The resulting genetic circuits can be switched on and off applying presently-accepted prescription drugs, which makes it possible for researchers to control when and the place the hacked T cells are lively, as perfectly as their production of a protein named IL-2 which stimulates immune responses.
The other team of researchers, led by synthetic biologist Wendell Lim at the University of California, San Francisco, programmed Automobile T cells to deliver IL-2 only when the engineered T cell encounters a most cancers mobile. The group uncovered that this IL-2 output was most effective at fighting tumours in mice with pancreatic cancer when it was activated by way of a pathway that was individual from the a person made use of to figure out the cancer cell — a depth that could help in shaping foreseeable future therapies, suggests Andrea Schietinger, a tumour immunologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York Metropolis.
Sound progress
Both equally strategies could be specifically useful in crafting Auto-T therapies that can concentrate on good tumours, Schietinger says. Stable tumours have posed a unique obstacle to Motor vehicle-T approaches due to the fact the engineered cells have issues infiltrating the tumours and, the moment there, can be disabled by indicators that cancer cells use to suppress the immune reaction. “These engineered T cells prevail over both equally roadblocks,” she suggests. “They uncover their way in and then, once they are in, get the signals in the ideal area and at the proper time to be really powerful in killing the most cancers mobile.”
The capability to transform the T cells on and off could also aid to reduce a phenomenon termed T-cell exhaustion, in which T cells become inactive just after a prolonged period of stimulation, suggests Evan Weber, a cancer immunologist at the Children’s Clinic of Philadelphia in Pennsylvania. Some research have found that providing T cells a ‘rest period’ can minimize T mobile exhaustion and strengthen their total efficiency in opposition to tumours3.

Constructing far better Car or truck-T therapies
Lim ideas to additional develop the technique for screening in clinical trials, and to tweak it to investigate the results of making other molecules that, like IL-2, encourage immune cells. There has been a escalating realization that this sort of molecules, known as cytokines, could be pivotal to the success of Vehicle-T therapies, suggests Weber. “We know we need smarter strategies of tapping into them,” he says, “rather than just turning on a receptor all the time or secreting a cytokine constitutively.”
Khalil hopes that the program that he and his colleagues have designed will be usable in other cell styles, including a different type of immune mobile termed macrophages, which are superior than T cells at penetrating reliable tumours. His genetic circuits were developed with adaptability in mind, so that researchers who specialize in cancer immunotherapies — or fields such as gene treatment or stem-cell biology — can tweak them to suit their needs. “I hope this will seize the creativity of a good deal of scientists out there,” he suggests.








